How Joints Work – The Ultimate Guide
Joints are where two bones meet, allowing our bodies to move in many ways. Some joints, like those in your skull, barely move at all, while others, like the ones in your shoulders and hips, move freely in many directions. The ends of bones are usually covered with a smooth surface to help them glide easily against each other. When muscles contract, they pull on bones, causing the joints to move. This movement is essential for everything from walking and jumping to waving and typing.
However, joints can also be sources of pain and stiffness, especially as we age or if we injure them. The thick connective tissue that helps hold joints together and attach muscles to bones can become inflamed, leading to pain and swelling. Understanding how joints work and how to care for them can help keep them healthy and functional for as long as possible.
There are many different types of joints in the human body, each designed for specific movements and degrees of motion. For example, the joints between the bones of the skull are very different from those between the tibia and fibula or the hip bones. By learning about the various types of joints and how they function, you can gain a deeper appreciation for the complexity and wonder of the human body.
Protecting joint health is crucial for maintaining mobility and quality of life. This involves regular exercise, maintaining a healthy weight, and avoiding injuries. Additionally, understanding the signs of joint conditions and seeking prompt treatment can prevent further damage and preserve joint function. By taking care of your joints, you can enjoy a wide range of activities and keep moving smoothly throughout your life.
Whether you’re interested in biology, looking to understand your own body better, or seeking ways to take care of your joints, this guide will provide valuable insights. From the basics of joint anatomy to tips for maintaining joint health, you’ll find comprehensive information designed to help you embrace the complexity of joint anatomy for better health.
The Foundation of Joint Anatomy
The foundation of joint anatomy begins with understanding the basic building blocks: bones and connective tissue. Thick connective tissue plays a vital role in forming joints, connecting bone to bone, and providing the necessary support and stability for movement. For example, the syndesmosis joint between the tibia and fibula, as well as the connections between hip bones, showcases the diversity and specialization in joint construction. Moreover, the bones of the skull, while largely immobile, are connected by joints crucial for protecting the brain and forming the structure of our faces. This foundational knowledge sets the stage for exploring the more intricate aspects of how joints facilitate movement and contribute to our overall mobility.
Diving Into the Basics: What Are Joints?
Joints are the points where two or more bones meet, allowing for movement and support. Without joints, our skeletal system would be rigid, making movements like bending, turning, or even walking impossible. The bones of the skull, for example, have joints between them that are mostly immobile, providing a solid case to protect the brain. In contrast, the joints between the tibia and fibula in the leg offer a different type of movement, demonstrating the variety in joint function and structure throughout the body.
Similarly, the hip bones are connected by joints that allow for a wide range of motion, enabling actions such as walking, sitting, and bending. This diversity in joint types and their specific functions highlights the incredible adaptability and complexity of the human body. By understanding the basic forms and functions of joints, you can better appreciate the intricate dance of bones, muscles, and connective tissues that keeps us moving every day.
Moreover, joints not only facilitate movement but also bear the weight of our bodies, absorb shock, and maintain our structure. The design of each joint reflects its role in the body, from the relatively simple structure connecting the bones of the skull to the complex mechanisms that allow your hips to swivel and your knees to bend. Recognizing the basic components and types of joints is the first step towards understanding the broader picture of human anatomy and movement.
Joint Classification: Structural and Functional Insights
Joint classification provides insight into how our bodies move and function. Joints are categorized based on their structure and the type of movement they allow. For example, the way a bone fits into another bone in the shoulder and hip joints allows for a wider range of motion compared to the single plane movement of joints in the vertebral column. Additionally, the presence of intervertebral discs between the bones in the spine offers flexibility and acts as a cushion, demonstrating the functional importance of understanding joint types. This classification helps us grasp the diversity of joint functions and their critical roles in enabling movement and providing stability to the skeletal system.
Understanding Fibrous Joints
Fibrous joints are characterized by the absence of a joint cavity, with bones held closely together by fibrous connective tissue. This type of joint is exemplified by the sutures in the bones of the skull, where the edges of bones grow together over time to protect the brain. Similarly, the connection between the tibia and fibula in the leg features a syndesmosis joint, a type of fibrous joint that allows for slight movement and provides stability, especially during walking or running.
The fibrous joints between hip bones, although less prominent, play a crucial role in supporting the body’s weight and maintaining posture. These joints are designed for strength and protection, rather than for flexibility. The dense connective tissue that binds these bones together is incredibly strong, ensuring that the bones do not move apart from each other, which is essential for the stability of the pelvic region.
Understanding fibrous joints helps us appreciate the balance between movement and stability in the human body. While these joints do not offer much in terms of flexibility, they are critical for protecting vital organs and providing a sturdy framework for our bodies. This insight into fibrous joints reveals the complexity of joint anatomy and the specialized functions that different types of joints serve in our skeletal system.
Exploring Cartilaginous Joints
Cartilaginous joints are where bones are joined together by cartilage, allowing for more movement than fibrous joints but less than synovial joints. A key example is the connection between the tibia and fibula, which, while primarily considered a fibrous joint, also showcases characteristics similar to cartilaginous joints at certain points, providing slight flexibility and shock absorption. These joints are crucial for maintaining stability while also permitting necessary movement, especially in areas of the body that bear significant weight or undergo frequent motion.
While the bones of the skull do not typically feature cartilaginous joints, understanding the role of cartilage in other parts of the body helps us appreciate the diversity of joint structures. Cartilage acts as a cushion between bones, reducing friction and absorbing shock during movements such as walking, running, or jumping. This property is particularly important in joints that must withstand high levels of stress, providing both flexibility and resilience.
The exploration of cartilaginous joints underscores the importance of cartilage in joint function and health. By understanding how these joints work, we gain insights into how our bodies achieve a balance between movement and stability, and how they manage the stresses of daily activities. This knowledge is essential for anyone looking to maintain joint health and prevent injuries, highlighting the vital role of cartilage in our overall well-being.
The Dynamics of Synovial Joints
Synovial joints are the most mobile type of joint in the human body, featuring a joint capsule that contains synovial fluid. This fluid lubricates the joint, reducing friction and allowing for smooth movement. The bones of the skull, while not synovial, provide a contrast that highlights the unique properties and functions of synovial joints. These joints enable a wide range of movements, from the simple opening and closing of a hinge joint to the complex rotations and swiveling actions of ball-and-socket joints.
The design of synovial joints includes several key features that ensure their functionality and longevity. The joint capsule encloses the joint, providing structural support, while the synovial membrane within the capsule produces synovial fluid for lubrication. Additionally, cartilage covers the ends of bones within the joint, further reducing friction and absorbing shock. This intricate combination of features allows synovial joints to facilitate movement efficiently and comfortably.
Understanding the dynamics of synovial joints sheds light on how our bodies achieve the remarkable range of motion necessary for daily activities and athletic endeavors. These joints are central to our ability to move freely, and their health is crucial for maintaining an active and pain-free lifestyle. By exploring the structure and function of synovial joints, we gain a deeper appreciation for the complexity and sophistication of the human body’s design.
The Intricacies of Synovial Joints
The complexities of synovial joints extend beyond their basic structure to include a variety of features that enhance their function and resilience. The presence of additional structures such as tendons, ligaments, and bursae within and around synovial joints contributes to their versatility and durability. These components work together to provide strength, flexibility, and protection against wear and tear, showcasing the intricate design that enables our joints to handle the demands of movement and support. Understanding these intricacies offers valuable insights into how synovial joints operate and adapt to the challenges of daily activities and athletic performance.
The Core Structural Features of Synovial Joints
Synovial joints are distinguished by their unique structure, designed to facilitate a wide range of movements while providing stability and support. At the heart of a synovial joint is the joint capsule, a tough outer layer that encloses the joint and maintains its integrity. Inside the capsule, the synovial membrane produces synovial fluid, a lubricant that minimizes friction and wear within the joint during movement.
Another key feature of synovial joints is the cartilage that covers the ends of bones, providing a smooth, durable surface that resists wear and absorbs shock. This cartilage is crucial for ensuring that movements are fluid and pain-free. Additionally, surrounding ligaments and tendons contribute to the joint’s stability by connecting bones to each other and to muscles, enabling controlled, coordinated movements.
The combination of these core features allows synovial joints to function efficiently under a wide range of conditions and activities. From the gentle glide of a wrist turning to the powerful thrust of a leg kicking, synovial joints enable the complex and varied movements that are essential to our daily lives. By understanding the structure and function of these joints, we can better appreciate the remarkable capabilities of the human body and the importance of maintaining joint health for overall mobility and quality of life.
Beyond the Basics: Additional Structures Associated with Synovial Joints
Synovial joints are like the busy hubs of your body’s movement, allowing you to twist, turn, and tackle daily tasks with ease. But, there’s more to these joints than just bones meeting each other. Take the fluid-filled sacs, for instance, nestled in places where muscles or skin might rub against bone. These sacs are filled with lubricating fluid, making movements smoother and preventing your joints from wearing out. Especially in weight-bearing joints like the knee, these sacs play a crucial role in keeping you on the move without pain.
Another key player in the complex world of synovial joints is the fat pad. Positioned strategically to cushion and protect, fat pads absorb shocks and impacts, safeguarding the bones of the joint and the underlying bone. This is particularly important in joints that bear a lot of weight, ensuring that each step you take is as comfortable as possible.
Lastly, the synovial joints of the body strongly unite through structures designed to support and stabilize. The radius and ulna bones in your arm, for example, work together, allowing for a range of movements from twisting the doorknob to throwing a ball. This teamwork is supported by the harmonious function of these additional structures, ensuring that each joint works smoothly and efficiently.
A Closer Look at Types of Synovial Joints
Picture the diverse range of movements your body can perform, from the delicate act of typing on a keyboard to the powerful motion of jumping high. This versatility is thanks to the various types of synovial joints, each with a unique structure and function. Pivot joints allow for rotation, like turning your head side to side, while hinge joints enable bending and straightening motions, such as in your knees and elbows. Then there are the ball-and-socket joints, the stars of mobility, found in your hips and shoulders, allowing for sweeping movements in almost every direction. Each joint, protected by hyaline cartilage and encased in an articular capsule, is a marvel of engineering designed to enhance mobility and keep you moving fluidly.
Pivot and Hinge Joints: Movement and Mechanics
Pivot and hinge joints are the unsung heroes that allow for the simple yet essential movements you perform daily. Imagine turning your head to look over your shoulder; that’s your pivot joint in action, enabling rotation around a single axis. Now think about bending your elbow to lift a glass of water; that’s your hinge joint working, allowing movement in one direction. These joints, with their straightforward mechanics, are fundamental to your body’s ability to move with precision and purpose.
The design of pivot and hinge joints is all about efficiency and specificity. In a pivot joint, a ring of bone fits around a protruding axis, giving you the ability to rotate your forearm. Hinge joints, on the other hand, work like the hinges on a door, ensuring movements are controlled and stable. This specificity in design underscores the body’s incredible ability to tailor each joint to its intended function, ensuring that whether you’re typing, running, or reaching out, your movements are smooth and coordinated.
Despite their simplicity, these joints are built to withstand considerable stress, supporting your body’s weight and absorbing impact as you go about your day. The robustness of these joints, combined with their specialized mechanics, make them integral to maintaining a healthy and active lifestyle, allowing you to move freely and without discomfort.
Condyloid, Saddle, and Plane Joints: Their Unique Functions
Condyloid, saddle, and plane joints might not be as well-known as their synovial cousins, but their contributions to your body’s mobility are just as significant. Each of these joints has a unique way of facilitating movement that’s tailored to specific tasks. Condyloid joints, for example, allow movement in two directions, like the wrist when you’re typing or painting, offering a blend of flexibility and control.
Saddle joints take this a step further, providing an even greater range of motion. Think of the thumb’s base; this saddle joint lets you grip and grasp, giving your hands their dexterous capability. Then there are the plane joints, the unsung heroes of subtle movements, found between the carpal bones in the palm of your hand. These joints allow for the gliding motions that add precision to your grip.
Despite their differences, these joints share a common goal: enhancing your mobility and dexterity. Whether it’s the condyloid joint’s versatility, the saddle joint’s intricate movements, or the plane joint’s smooth gliding, each plays a crucial role in your body’s complex system of movement, showcasing the incredible adaptability and functionality of the human body.
The Versatility of Ball-and-Socket Joints
Ball-and-socket joints stand out as the champions of movement in the human body, offering a range of motion that’s as broad as it is versatile. These joints, found in your shoulders and hips, support movements in multiple directions and planes, from swinging a tennis racket to performing a ballet pirouette. The spherical head of one bone fits into the cup-like socket of another, allowing for rotational movements and side-to-side flexibility that other joint types simply can’t match.
This versatility doesn’t come at the expense of strength or stability. The deep socket, strong ligaments, and surrounding muscles work together to keep the joint secure while allowing for dynamic movements. This balance is what lets you engage in a wide array of physical activities, from high-impact sports to intricate dance movements, with both power and grace.
The ball-and-socket joint’s design is a testament to the body’s evolutionary ingenuity, providing the perfect blend of flexibility, strength, and range of motion. It’s this unique combination that enables the fluid, expansive movements that define the human capacity for physical expression, making these joints a key player in everything from daily tasks to extraordinary athletic feats.
Understanding How Joints Function
Joints are the pivot points that allow your body to move in various ways, acting like the hinges and bearings that keep everything connected and moving smoothly. They’re made up of bones, ligaments, cartilage, and synovial fluid, working together to support your body’s weight and enable a wide range of movements. From the simple act of walking to the complex mechanics of throwing a ball, joints are at the heart of every movement you make.
The functionality of joints goes beyond mere movement; they also play a crucial role in bearing weight and providing structural support. Whether you’re standing still or performing a high jump, your joints are working overtime to balance and stabilize your body, ensuring each motion is as efficient and pain-free as possible. This is especially true for the weight-bearing joints in your hips, knees, and spine, which absorb impact and distribute weight evenly throughout your body.
Understanding how joints function is essential for maintaining a healthy, active lifestyle. Keeping your joints healthy means you can continue enjoying your favorite activities without discomfort or limitation. Regular exercise, a balanced diet, and proper care can help preserve joint health, ensuring that your body’s system of movement remains smooth and coordinated for years to come.
The Role of Joints in Human Movement
Joints are in the human body to make sure you can move freely and with ease. Think of them as the connectors that allow your bones to work together, bending, twisting, and turning in every direction possible. Without joints, movements like walking, jumping, or even waving would be impossible. They are the reason you can dance, play sports, and do just about anything that involves moving.
Each joint in your body has a specific role, depending on its location and the type of movement it supports. For example, the joints in your fingers allow for precise movements like typing or playing an instrument, while the joints in your knees provide the stability and strength needed for walking and running. This specialization ensures that every part of your body works together seamlessly, allowing for smooth, coordinated movements.
By understanding the role of joints in human movement, you can appreciate the complexity and beauty of your body’s design. It’s a reminder of how important it is to take care of your joints through regular exercise, proper nutrition, and avoiding activities that could harm them. Doing so will help keep your joints healthy and functional, ensuring that you can move freely and enjoy an active lifestyle for years to come.
How Many Joints Are in the Human Body? A Quantitative Overview
Have you ever wondered how many joints are in the human body? The answer might surprise you – the human body is home to over 300 joints! These range from the large, complex joints like those in your hips and knees to the smaller ones in your fingers and toes. Each joint plays a vital role in providing mobility and flexibility, allowing you to perform a wide range of activities with ease.
This vast array of joints works together to support your body’s movements, from the most basic to the most complex. The variety of joints, including ball-and-socket, hinge, pivot, and more, ensures that you can engage in activities as diverse as running, swimming, lifting, and writing. The complexity and number of joints also highlight the incredible adaptability and versatility of the human body, capable of movements that are precise, powerful, and graceful.
Understanding the sheer number of joints in the human body underscores the importance of joint health. Keeping these joints functioning properly through regular exercise, proper nutrition, and preventative care can help ensure that you remain active and pain-free. It’s a fascinating aspect of human anatomy that showcases the intricate balance between structure and function, enabling the wide range of human movement and activity.
Common Conditions Affecting Joint Health
Joints, the vital connectors that allow for movement and flexibility in the human body, can sometimes be affected by various conditions, leading to discomfort and limited mobility. Common issues include arthritis, a term that encompasses several conditions causing pain and inflammation in the joints. Osteoarthritis results from wear and tear over time, while rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disease where the immune system attacks the joints.
Injuries to the joints, such as sprains, strains, and fractures, can also impact their health and functionality. These injuries often occur during physical activities or accidents and can range from mild to severe, affecting not just the bones but also the ligaments, tendons, and muscles that support the joints. Proper treatment and rehabilitation are crucial for recovery and preventing long-term damage.
Maintaining joint health is essential for leading an active and fulfilling life. Regular exercise, a balanced diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods, and avoiding excessive strain can help prevent many common joint issues. For those already experiencing joint problems, medical interventions, physical therapy, and sometimes surgery can offer relief and restore mobility. Understanding and addressing the factors that affect joint health are key steps in ensuring your joints stay healthy and functional throughout your life.
Identifying Common Joint Conditions and Their Symptoms
When you think about joint issues, a few common conditions likely come to mind. Arthritis, which includes both osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis, is one of the most prevalent joint issues many people face. Osteoarthritis happens when the cartilage that cushions the ends of bones wears down over time, leading to pain, stiffness, and reduced movement. Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disorder where the body’s immune system attacks its tissues, causing inflammation in the joints. Symptoms of arthritis include swelling, pain, stiffness, and decreased range of motion.
Another joint condition to be aware of is bursitis, which occurs when the bursae, the small, fluid-filled sacs that cushion the bones, tendons, and muscles near joints, become inflamed. Symptoms often include pain at the site of the joint, especially when the joint is moved or pressure is applied. Lastly, tendinitis, an inflammation of the tendons, can cause pain and tenderness just outside a joint. Common areas for tendinitis include the shoulder, elbow, knee, and heel.
Identifying these conditions early is crucial for effective management. Paying attention to signs like persistent joint pain, swelling, and stiffness can help you seek timely medical advice. Remember, these symptoms can also vary in intensity and might not be present all the time, depending on the condition’s severity and the joint affected.
Diagnostic Approaches: How Are Joint Conditions Assessed?
Diagnosing joint conditions often starts with a thorough medical history and physical examination. Your doctor will ask about your symptoms, any previous injuries, and your family history of joint issues. They will look for signs of inflammation, check the range of motion, and assess the pain in the affected joint. This initial assessment helps narrow down the possible causes of your joint problems.
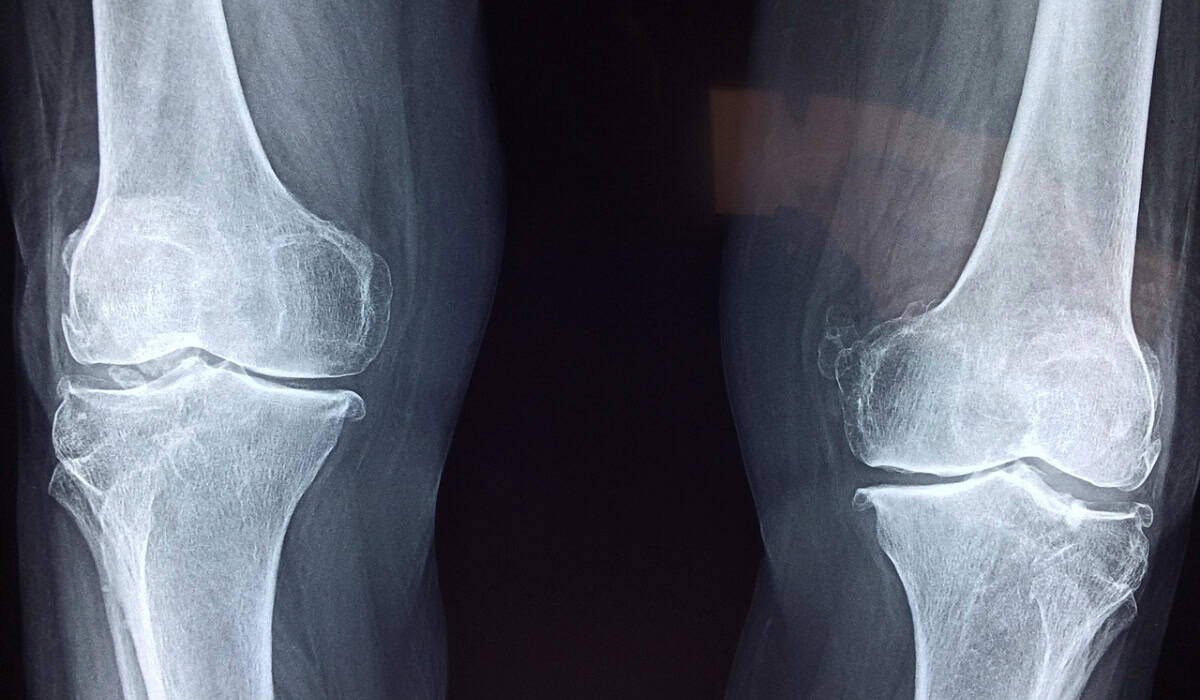
Following the physical exam, imaging tests like X-rays, MRIs, or CT scans may be used to get a closer look at the structure of your joints. These tests can reveal details about the bone, cartilage, and other tissues inside the joint, helping to identify specific issues like the extent of arthritis or any injury. Sometimes, blood tests are also conducted to check for markers of inflammation or infection that could be contributing to joint pain.
In certain cases, your doctor might recommend a more direct examination of the joint through procedures like arthroscopy. This involves inserting a small camera into the joint space to get a clear view of the inside, allowing for a more accurate diagnosis. By combining these approaches, healthcare providers can effectively identify the underlying cause of joint discomfort and tailor treatment plans accordingly.
Practical Tips for Joint Care and Maintenance
Taking care of your joints is essential for maintaining mobility and quality of life. One easy but effective tip is to stay active. Regular, low-impact exercises like walking, swimming, or cycling can help keep your joints flexible and strengthen the muscles around the joints. Strength training is also beneficial, as it helps support and protect the joints by reinforcing the muscles and tissues that surround them.
Maintaining a healthy weight is another critical aspect of joint care. Excess weight puts additional pressure on your joints, especially those that bear weight like your hips, knees, and ankles. The Cleveland Clinic suggests that even a small amount of weight loss can significantly reduce joint pain and prevent further damage.
Lastly, it’s important to listen to your body. If certain activities or movements cause joint pain, try to modify or avoid them. Use assistive devices if necessary to reduce strain on your joints during daily tasks. And, don’t forget to give your joints the rest they need, balancing activity with periods of rest to prevent overuse and inflammation.
Enhancing Your Knowledge on Joints
Understanding how your joints work and how to keep them healthy is crucial for everyone, not just those currently experiencing problems. One way to enhance your knowledge is by exploring the mechanics of movement. This includes learning how different types of joints allow for various movements and how muscles and ligaments work together to support and move your joints.
Another key area is understanding the impact of lifestyle choices on joint health. This encompasses not only the importance of regular exercise, including strength training, but also the role of nutrition in maintaining healthy joints. Consuming a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals supports overall health and can help prevent joint issues.
Lastly, staying informed about the latest research and treatment options for joint conditions is beneficial. Advancements in medical science offer new insights and therapies for managing joint health, from innovative exercise regimens to cutting-edge medical treatments. Engaging with reputable sources and healthcare professionals can help you stay ahead in the care and maintenance of your joints.
Recommended Exercises to Support Joint Health
Supporting your joints through exercise is a key component of joint health. Low-impact aerobic exercises like walking, swimming, and cycling are excellent for improving blood circulation and reducing stiffness without putting too much strain on your joints. Incorporating these activities into your routine can also help with weight management, which is crucial for reducing the load on weight-bearing joints.
Strength training is another important aspect of joint support. Exercises that target the major muscle groups can help stabilize and protect your joints by strengthening the muscles around them. It’s important to focus on proper form and to start with lighter weights, gradually increasing the intensity to avoid injury.
Flexibility and stretching exercises are also beneficial for maintaining a good range of motion in your joints. Yoga and Pilates, for example, can improve flexibility, balance, and core strength, all of which contribute to joint health. Remember, consistency is key, and it’s important to find a balanced routine that includes aerobic, strengthening, and flexibility exercises.
A Summary of Learning Objectives and Review Questions
By now, you should have a better understanding of how joints work, common joint conditions and their symptoms, and how these conditions are diagnosed and treated. You’ve also learned practical tips for joint care and maintenance, including the importance of exercise and weight management. Finally, you’ve explored ways to enhance your knowledge on joint health. To further solidify your learning, consider how bones are connected and the role of the spinal cord in facilitating movement. What are the benefits of low-impact exercises for joint health? How does maintaining a healthy weight affect joint function?
Interactive Learning Resources and External Websites for Deeper Understanding
For those interested in deepening their understanding of joint health, several interactive learning resources and external websites are available. Websites like the Arthritis Foundation offer detailed information on different types of joint conditions, tips for managing pain, and ways to stay active safely. They also provide tools and apps designed to help track symptoms and progress over time.
Additionally, educational platforms offer interactive courses and videos on anatomy and physiology, including the mechanics of joints and how they’re affected by various diseases. These resources often include visual aids like diagrams and 3D models that can help visualize the complex structures of joints and how they work.
For individuals considering or recovering from joint replacement surgery, specific resources are tailored to guide you through the process. These include recovery exercises, tips for post-surgery care, and forums where you can connect with others who have undergone similar procedures. Leveraging these resources can provide valuable support and insights, enhancing your journey toward joint health and recovery.
Conclusion: Embracing the Complexity of Joint Anatomy for Better Health
Understanding how your joints work is crucial for keeping them healthy. Every joint is functionally classified based on how it moves, like bending your knee or rotating your shoulder. This knowledge isn’t just for doctors or athletes. By integrating it into your daily routine, you can make smarter choices about your activities and how to protect yourself from sports injuries. Remember, each movement you make, whether it’s reaching for a cart at the grocery store or jogging in the morning, involves the complex mechanics of your joints.
Joint health is not something to take lightly. The dense connective tissue that helps hold your joints together can be susceptible to wear and tear over time. This is why it’s important to listen to your body and not push through pain during exercise or daily activities. There are many resources available, such as a health library, where you can learn more about how to care for your joints and recognize the signs of potential problems early on.
Preventative care is key. Simple habits can make a big difference, like warming up before exercise, incorporating foods that support joint health into your diet, and staying active to maintain flexibility and strength around your joints. If you ever experience joint pain, methods like joint aspiration, where fluid is removed from around the joint for testing, can help diagnose the issue. Don’t hesitate to seek professional advice to keep your joints healthy.
Finally, embracing the complexity of joint anatomy encourages a proactive approach to health. By understanding the basics of how your joints work and taking steps to protect them, you can enjoy a more active and pain-free life. Remember, taking care of your joints is an investment in your overall health and well-being. Start today, and your body will thank you tomorrow.